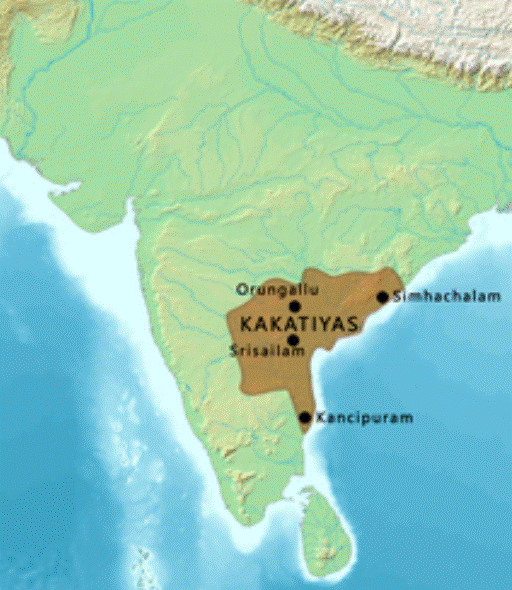
|
The Kakatiya dynasty (Kākatīya)[a] was
a Telugu dynasty that ruled most of eastern Deccan region
in present-day India between 12th and 14th centuries. Their territory
comprised much of the present day Telangana and Andhra
Pradesh, and parts of eastern Karnataka,
northern Tamil Nadu, and southern Odisha. Their
capital was Orugallu, now known as Warangal. Early Kakatiya rulers served as feudatories to Rashtrakutas and Western
Chalukyas for more than two centuries. They assumed sovereignty
under Prataparudra I in 1163 CE by suppressing other Chalukya subordinates in
the Telangana region. Ganapati Deva (r. 1199–1262) significantly expanded
Kakatiya lands during the 1230s and brought under Kakatiya control the
Telugu-speaking lowland delta areas around the Godavari and Krishna rivers.
Ganapati Deva was succeeded by Rudrama Devi (r.
1262–1289) who is one of the few queens in Indian history. Marco
Polo, who visited India around 1289–1293, made note of Rudrama
Devi's rule and nature in flattering terms. She successfully repelled the
attacks of Yadavas (Seuna) of Devagiri into the Kakatiyan territory. In 1303, Alauddin Khalji, the emperor of the Delhi
Sultanate invaded the Kakatiya territory which ended up as a
disaster for the Turks. But after the successful siege of
Warangal in 1310, Prataparudra II was forced to pay annual tribute to
Delhi. Another attack by Ulugh Khan in
1323 saw stiff resistance by the Kakatiyan army, but they were finally
defeated. The demise of Kakatiya dynasty resulted in confusion and anarchy
under alien rulers for sometime, before Musunuri Nayaks united
the various Telugu clans and recovered Warangal from
the Delhi Sultanate. Kakatiyas unified the distinct upland and lowland cultures of
Telugu lands, which brought into being a feeling of cultural affinity between
those who spoke the Telugu language. Kakatiya period also
saw the construction of reservoirs for irrigation in the uplands called
"tanks" many of which are still used today. They were egalitarian
in nature and anyone, regardless of birth, could acquire the nayaka title
that denoted the warrior status. They recruited peasants into the military
which resulted in a new warrior class and provided social mobility. Kakatiya
era also saw the development of a distinct style of architecture which
improved and innovated upon the existing modes. Most notable examples are the Thousand
Pillar Temple in Hanamkonda, Ramappa
Temple in Palampet, Warangal Fort, Golconda
Fort and Kota Gullu in Ghanpur. From Wikipedia |